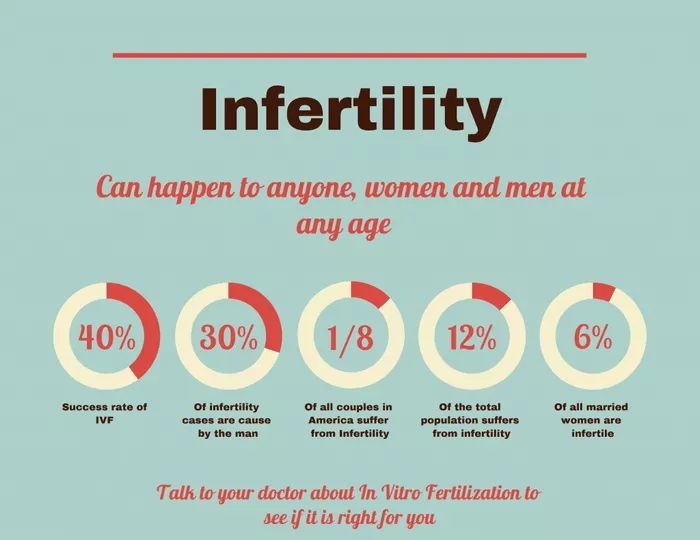
Infertility can be a challenging and emotionally taxing journey for individuals and couples who are trying to conceive. While many factors can contribute to infertility, understanding the underlying causes is crucial for seeking appropriate treatment and support. In this article, we’ll explore the various factors that can lead to infertility, shedding light on this complex issue and offering insights into potential solutions.
Genetic Factors: Unraveling the Genetic Code
Genetic factors can play a significant role in infertility, affecting both male and female reproductive health. Just as a glitch in a computer program can cause errors, genetic abnormalities or mutations can impact fertility by interfering with the production or function of reproductive cells. Conditions such as chromosomal abnormalities, genetic disorders, and gene mutations can affect sperm or egg quality, leading to infertility or recurrent pregnancy loss.
Hormonal Imbalances: Balancing the Body’s Chemistry
Hormonal imbalances can disrupt the delicate balance of hormones needed for normal reproductive function. Just as a symphony requires perfect harmony among its instruments, the reproductive system relies on precise hormonal signaling to regulate ovulation, sperm production, and menstrual cycles. Conditions such as polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS), thyroid disorders, and adrenal gland disorders can disrupt hormonal balance, affecting fertility in both men and women.
Structural Issues: Examining the Anatomy
Structural abnormalities or disorders of the reproductive organs can also contribute to infertility. Just as a flaw in the design of a building can compromise its stability, structural issues such as blocked fallopian tubes, uterine fibroids, or varicoceles (enlarged veins in the scrotum) can interfere with conception or pregnancy. These conditions may require surgical intervention or assisted reproductive technologies (ART) to address and improve fertility outcomes.
Lifestyle Factors: Navigating the Modern World
Lifestyle factors can significantly impact fertility, often reflecting the demands and stressors of modern life. Just as a well-tuned engine requires proper maintenance, the human body thrives on healthy habits and routines. Factors such as smoking, excessive alcohol consumption, poor nutrition, obesity, and stress can all negatively affect fertility by disrupting hormone levels, sperm production, or ovulation. Making lifestyle changes, such as adopting a healthy diet, exercising regularly, and reducing stress, can improve fertility outcomes and overall reproductive health.
Environmental Exposures: Facing External Challenges
Exposure to environmental toxins and pollutants can also affect fertility by disrupting reproductive function. Just as pollution can harm the environment and wildlife, exposure to chemicals, pesticides, heavy metals, and radiation can impact fertility in both men and women. Occupational hazards, environmental pollution, and lifestyle factors such as smoking or drug use can all contribute to infertility by damaging reproductive cells or interfering with hormone production.
Age-related Factors: Confronting the Biological Clock
Age is a significant factor in fertility, particularly for women. Just as a ticking clock marks the passage of time, a woman’s fertility declines with age, particularly after the age of 35. As women age, the quantity and quality of their eggs decrease, making it more challenging to conceive naturally and increasing the risk of miscarriage and pregnancy complications.
Medical Conditions and Treatments: Managing Health Challenges
Certain medical conditions and treatments can impact fertility or interfere with reproductive function. Just as a medical condition requires appropriate treatment, conditions such as cancer, autoimmune disorders, diabetes, and sexually transmitted infections (STIs) can affect fertility by damaging reproductive organs or interfering with hormone production. Additionally, treatments such as chemotherapy, radiation therapy, and certain medications can impair fertility or cause temporary or permanent infertility.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, infertility is a complex and multifaceted issue with various potential causes. Understanding the underlying factors contributing to infertility is essential for individuals and couples seeking to overcome fertility challenges and achieve their dream of parenthood. By addressing genetic, hormonal, structural, lifestyle, environmental, age-related, and medical factors, individuals can take proactive steps to optimize their reproductive health and explore fertility treatment options that best suit their needs and circumstances.
[inline_related_posts title=”You Might Be Interested In” title_align=”left” style=”list” number=”6″ align=”none” ids=”1706,1710″ by=”categories” orderby=”rand” order=”DESC” hide_thumb=”no” thumb_right=”no” views=”no” date=”yes” grid_columns=”2″ post_type=”” tax=””]