Fertility is a topic of significant interest and concern for many people, especially for those planning to start a family. While much focus is often placed on female fertility, understanding male fertility is equally important. Male fertility is influenced by various factors, including age. In this article, we will delve into when a man is most fertile, the biological aspects of male fertility, and factors that can affect it. Our goal is to provide a comprehensive overview to help readers understand the peak fertility period for men and the implications of age on male reproductive health.
Male Reproductive System and Sperm Production
Before discussing the peak fertility age, it is essential to understand how the male reproductive system works. The primary organs involved in male reproduction are the testes, which produce sperm and the hormone testosterone. Sperm production, or spermatogenesis, occurs in the seminiferous tubules within the testes. This process begins at puberty and continues throughout a man’s life, albeit with varying efficiency.
Spermatogenesis: The Lifelong Process
Spermatogenesis is a continuous process that takes about 64 days for a single sperm cell to develop. This process involves several stages, starting from spermatogonial stem cells that divide and differentiate into mature spermatozoa. Hormonal regulation plays a crucial role in spermatogenesis, with luteinizing hormone (LH) and follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH) being key regulators.
Peak Fertility Age in Men
Research indicates that men are most fertile between the ages of 20 and 30. During this period, sperm quantity and quality are generally at their highest. Several studies have shown that sperm motility, morphology, and concentration are optimal in this age range. This is because, at a younger age, the body is more efficient at producing high-quality sperm cells.
Factors Influencing Peak Fertility
Hormonal Levels:
Testosterone levels peak in early adulthood and play a critical role in maintaining sperm production. High testosterone levels contribute to better sperm quality and quantity.
Sperm Quality:
Sperm motility, which refers to the sperm’s ability to swim effectively, is crucial for fertilization. Younger men tend to have higher sperm motility. Similarly, sperm morphology, which refers to the size and shape of sperm, is generally better in younger men.
Lifestyle Factors:
A healthy lifestyle, including a balanced diet, regular exercise, and avoidance of smoking and excessive alcohol consumption, contributes to optimal sperm production. Younger men are more likely to engage in healthier lifestyle practices.
Impact of Aging on Male Fertility
As men age, several changes occur that can impact fertility. While men can produce sperm throughout their lives, the efficiency of sperm production and the quality of sperm decline with age. Here are some key changes that occur with aging:
Decreased Sperm Motility:
Sperm motility declines with age. This reduction in motility can make it more challenging for sperm to reach and fertilize an egg.
Lower Sperm Count:
The total number of sperm produced tends to decrease as men age. This decline can reduce the likelihood of successful fertilization.
Increased DNA Fragmentation:
Older sperm are more likely to have DNA damage. DNA fragmentation in sperm can lead to lower fertility rates and higher chances of miscarriage and genetic abnormalities in offspring.
Changes in Hormonal Levels:
Testosterone levels gradually decrease with age. Lower testosterone levels can affect spermatogenesis and reduce sperm quality.
Research Findings on Male Fertility and Age
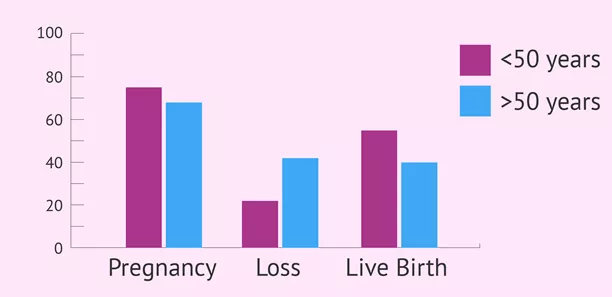
Several studies have highlighted the relationship between male age and fertility. For example, a study published in the journal Fertility and Sterility found that sperm motility and morphology significantly decline after the age of 40. Another study in the American Journal of Epidemiology reported that men over 45 are more likely to experience infertility issues compared to younger men.
Societal Implications and Trends
In modern society, many couples are choosing to start families later in life. This trend has led to increased interest in understanding the implications of paternal age on fertility and offspring health. While men remain fertile much longer than women, the decline in sperm quality with age means that delayed fatherhood can pose challenges.
Mitigating Age-Related Fertility Decline
Although aging affects male fertility, there are steps that men can take to mitigate these effects:
Maintain a Healthy Lifestyle:
Regular exercise, a balanced diet, and avoiding smoking and excessive alcohol can improve overall health and sperm quality.
Regular Health Check-ups:
Regular visits to a healthcare provider can help identify and address potential health issues that could affect fertility.
Consider Assisted Reproductive Technologies (ART):
For older men facing fertility challenges, ART options such as in vitro fertilization (IVF) and intracytoplasmic sperm injection (ICSI) can assist in achieving pregnancy.
Psychological and Emotional Considerations
The psychological and emotional aspects of male fertility are also important to consider. Men may experience stress and anxiety related to fertility issues, especially as they age. Open communication with partners and seeking support from healthcare professionals and counselors can help address these concerns.
Conclusion
Understanding the age-related aspects of male fertility is crucial for family planning and reproductive health. Men are most fertile between the ages of 20 and 30, a period characterized by optimal sperm quality and quantity. However, fertility declines with age due to changes in sperm motility, count, DNA integrity, and hormonal levels.
While societal trends show a tendency towards later fatherhood, it is important for men to be aware of the potential challenges associated with aging and fertility. By maintaining a healthy lifestyle and considering medical assistance when necessary, men can improve their chances of achieving successful pregnancies, even later in life. Open communication, regular health check-ups, and being informed about fertility can empower men to make proactive decisions about their reproductive health.
Related Links:
Understanding Male Infertility: Causes, Symptoms, Diagnosis, and Treatment Options