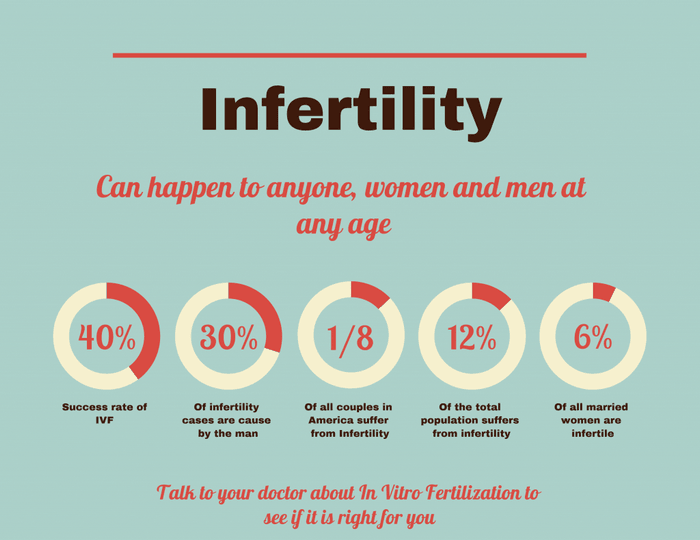
Infertility, often perceived as a condition primarily affecting women, has another, less discussed side. Infertility touches men and women equally, contributing to approximately 30-40% of all infertility cases globally. Understanding male infertility is hence integral to shed light on family planning, reproductive health, and the societal implications these hold. This article provides a comprehensive analysis of the reasons behind male infertility and how they can be addressed.
Male Infertility: Shattering the Taboo
Talking about male infertility is essential in breaking social stigmas and reinforcing the understanding that infertility is not a ‘woman’s problem’ but a human challenge.
Understanding Male Infertility
Male infertility is characterized by a man’s inability to cause pregnancy in a fertile female. It is typically associated with semen deficiencies, such as low sperm production, abnormal sperm function, or blockages preventing sperm delivery.
A Closer Look at the Causes of Male Infertility
Male infertility can stem from various causes. These include varicoceles, infection, ejaculation issues, tumors, hormone imbalances, chromosome defects, medications, prior surgeries, and environmental factors, among others.
Varicoceles: A Common Infertility Trigger
Varicoceles, an enlargement of the veins within the scrotum, are often implicated in male infertility. They can prevent normal cooling of the testicles, leading to a reduction in the quality and quantity of sperm.
Infections and Their Role in Male Infertility
Infections can interfere with sperm production and sperm health or cause scarring that blocks sperm’s passage. These include sexually transmitted infections, prostatitis, and mumps orchitis.
Ejaculation Issues and Infertility
Issues like retrograde ejaculation, ejaculatory duct obstruction, and hypospadias can cause male infertility by challenging the normal delivery of sperm.
Unforeseen Culprits: Tumors and Hormonal Imbalances
Tumors or cancer in the male reproductive system can significantly impact fertility. Simultaneously, hormonal imbalances can alter the various hormones necessary for sperm production, thereby affecting fertility.
Understanding Chromosome Defects and their Impact on Male Fertility
Certain genetic disorders can cause male infertility. These include Klinefelter’s syndrome, Kallmann syndrome, Kartagener syndrome, and cystic fibrosis.
The Role of Medications and Past Surgeries on Male Infertility
Certain medications can impact fertility. Similarly, surgeries like vasectomy, hernia repairs, and surgeries on the testicles, prostate, or other pelvic region may impact fertility significantly.
Environmental Causes: The Silent Impact
Environmental and lifestyle factors, including substance abuse, cigarette smoking, alcohol, excessive stress, obesity, and exposure to certain toxins, can decrease sperm count and overall fertility.
Diagnosis and Treatment of Male Infertility
Diagnosing male infertility involves a careful analysis of semen, hormonal evaluation, genetic testing, imaging, and testicular biopsy in some cases. Treatments can range from medication, assisted reproductive technologies, surgery to lifestyle modifications.
Counseling: An Essential Element in Managing Male Infertility
Infertility can take a toll on emotional health. Psychological counseling can provide invaluable support for men dealing with infertility, helping them manage relationships, self-esteem, and overall mental health.
Conclusion: A Contemporary Perspective on Male Infertility
Understanding the multifactorial issue of male infertility is a shared responsibility in couples wishing to conceive and is integral in cultivating a supportive environment for those affected. The journey to conception can be challenging for those facing infertility issues, underscoring the importance of early evaluation, a thorough understanding of causes, potential treatments, lifestyle modifications, and the need for emotional support and counseling.